参考
Spring Boot Docs
2.0: http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/#getting-started-installing-spring-boot
2.0: http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/html/
1.5: http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.x/reference/html/
Spring Boot Maven Plugins Docs
http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/maven-plugin/usage.html
前言
本文为作者的原创作品,转载需注明出处;
Requirement
这里我使用的是 Spring Boot 2.0.0 版本,要求 JDK 8.0 和 Spring 5.0.0 以上版本;
目的
通读 Spring Boot 官方文档,并形成一份阅读官网的手稿,做到边读边记录,并做出一些重点的批注;
Spring Boot CLI
Spring Boot CLI 是一个 Command Line Tool 帮助你快速构建 Spring Boot 应用;
安装
mac
1 | $ brew tap pivotal/tap |
Homebrew will install spring to /usr/local/bin.
Eclipse 配置
导入 Spring Boot 工程以前,需要首先在 Spring Boot 工程目录中执行mvn dependency:tree命令,自动导入 Spring Boot 的依赖包;然后再使用 Eclipse 导入 maven 工程;否则会有编译的错误
素材
Part III - Using Spring Boot
Starters
Starters are a set of convenient dependency descriptors that you can include in your application. You get a one-stop-shop for all the Spring and related technology that you need, without having to hunt through sample code and copy paste loads of dependency descriptors.
All official starters follow a similar naming pattern;
spring-boot-starter-*, where*is a particular type of application.all starters: http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/html/using-boot-build-systems.html#using-boot-starter
If you find that specific auto-configure classes are being applied that you don’t want, you can use the exclude attribute of
@EnableAutoConfigurationto disable them
1 | import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*; |
Chapter 17 - Spring Beans and dependency injection
If you structure your code as suggested above (locating your application class in a root package), you can add
@ComponentScanwithout any arguments. All of your application components (@Component, @Service, @Repository, @Controller etc.) will be automatically registered as Spring Beans.
constructor injection
1 | package com.example.service; |
And if a bean has one constructor, you can omit the @Autowired.
1 |
|
Chapter 18. Using the @SpringBootApplication annotation
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is equivalent to using @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan with their default attributes:
1 | package com.example.myproject; |
Chapter 19 Running Your Application
Running from Eclipse
我的思路如下,
通过 run configurations 配置
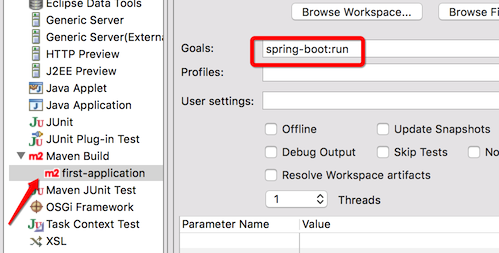
如果需要 debug,直接 Debug As … 即可。
Chapter 20 - Developer tools
- 提供了热启动和热部署
- 类似于 Grunt LiveReload 的 LiveReload 功能;
- Remote applications
这部分是精华了,- 可以通过 Client 的代码的变动,自动的将改动的代码 push 到 remote,触发热部署,热启动等
看看 20.5.2 Remote Update 小节的描述The remote client will monitor your application classpath for changes in the same way as the local restart. Any updated resource will be
pushedto theremoteapplication and (if required)trigger a restart.
强大,就相当于是直接用本地环境来开发服务器应用了… - 20.5.3 Remote Debug tunnel
开篇即说明了为什么要定义 Spring Boot 自己专有的 Remote debug 通道Java remote debugging is useful when diagnosing issues on a remote application. Unfortunately, it’s not always possible to enable remote debugging when your application is deployed
outside of your data center. Remote debugging can also be tricky to setup if you are using a container based technology such as Docker.
可见,如果你的 Client 和 Server 部署的不是在同一个数据中心(言外之意,因为防火墙的原因,不能够直接通过 TCP/IP 访问),那么通过 Java 默认的远程调试就困难重重了。正式因为如此,所以 Sprint Boot 提供了自己的远程调试模式,
To help work around these limitations, devtools supports tunneling of remote debug traffic over HTTP.
使用 HTTP 协议,避免防火墙等等限制…
我的思考,如果使用的 VPC 呢?HTTP 转发?需验证.
- 可以通过 Client 的代码的变动,自动的将改动的代码 push 到 remote,触发热部署,热启动等
Chapter 21. Packaging your application for production
Executable jars can be used for production deployment. As they are self-contained, they are also ideally suited for cloud-based deployment.
官网是建议直接通过 jars 来部署产品级应用的,不过如果部署的是 web 应用,要做到动静分离;所有静态资源还是需要放置在 nginx 上.
Part IV Spring Boot Features
23. SpringApplication
The SpringApplication class provides a convenient way to bootstrap a Spring application that will be started from a main() method.
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
FailureAnalyzers
如果启动失败,可以使用 FailureAnalyzers 进行分析,它可以将错误信息转换为 humman readable 的内容。
Application events and listeners
Web environment
SpringApplication 会自动的判断当前是否是 web 应用而选择不同的ApplicationContext,普通应用使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,web 应用使用 AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
It is often desirable to call setWebEnvironment(false) when using SpringApplication within a JUnit test.
Accessing application arguments
If you need to access the application arguments that were passed to
SpringApplication.run(…)you can inject aorg.springframework.boot.ApplicationArgumentsbean.
1 |
|
Using the ApplicationRunner or CommandLineRunner
If you need to run some specific code
oncethe SpringApplication has started, you can implement theApplicationRunnerorCommandLineRunnerinterfaces. Both interfaces work in the same way and offera single run methodwhich will be called just before SpringApplication.run(…) completes.
The CommandLineRunner interfaces provides access to application arguments as a simple string array
1 | import org.springframework.boot.* |
MyBean 在 SpringApplication.run(…) 结束以前执行,并且只会执行一次;String[] args 接收的是 SpringApplication.run(…) 中的参数,通常是通过命令行法启动的时候顺带输入的。
Application exit
DisposableBean@PreDestroyorg.springframework.boot.ExitCodeGenerator: to return a specific exit code when the application ends.
Admin features
spring.application.admin.enabled
This exposes the SpringApplicationAdminMXBean on the platform MBeanServer. You could use this feature to administer your Spring Boot application remotely. This could also be useful for any service wrapper implementation.
24 Externalized Configuration (外部化的配置)
Spring Boot allows you to externalize your configuration so you can work with the same application code in different environments.You can use
properties files,YAMLfiles,environment variablesandcommand-line argumentsto externalize configuration. Property values can be injected directly into your beans using the@Valueannotation, accessed via Spring’s Environment abstraction or bound to structured objects via@ConfigurationProperties.
意义在其引用的第一段话就说得非常明确了,Spring Boot 允许你通过外部化配置使得同一个应用在不同的环境中运行;
注意,后面,这里讲解了 17 种不同的配置方式,以及相应的加载顺序; 这里比较重要 http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/html/boot-features-external-config.html#boot-features-external-config
Configuring random values
Accessing command line properties
Application property files
SpringApplicationwill load properties fromapplication.propertiesfiles in the following locations and add them to the SpringEnvironment:
- A
/configsubdirectory of the current directory.- The current directory
- A classpath
/configpackage- The classpath root
The list is ordered by precedence (properties defined in locations higher in the list override those defined in lower locations). 彼此之间存在覆盖关系,从上到下依次加载,后面的覆盖前面的配置。
You can also use
YAML ('.yml')files as an alternative to ‘.properties’.
可以通过spring.config.name和spring.config.location配置配置文件的加载方式;
Profile-specific properties
In addition to
application.propertiesfiles, profile-specific properties can also be defined using the naming conventionapplication-{profile}.properties.特定环境的配置文件(Profile-specific)是通过
application-{profile}.properties的方式进行配置的。Profile-specific properties are loaded from the same locations as standard application.properties, with profile-specific files always overriding the non-specific ones irrespective of whether the profile-specific files are inside or outside your packaged jar.
Profile-specific properties 是从 application.properties 相同的位置进行加载的,Profile-specific files 总是会覆盖非特定环境的配置文件( non-specific ones ) 而无论 Profile-specific files 是在 jar 文件的内部还是在外部定义的。
Placeholders in properties
1 | app.name=MyApp |
注意,只可以引用前面定义好的属性;
Using YAML instead of Properties
YAML is a superset of JSON, and as such is a very convenient format for specifying hierarchical configuration data
Loading YAML
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean自动加载YAML为PropertiesYamlMapFactoryBean自动加载YAM为Map
1 | environments: |
转成 properties 如下,
1 | environments.dev.url=http://dev.bar.com |
1 | my: |
转换成 properties
1 | my.servers[0]=dev.bar.com |
可以通过@ConfigurationProperties加载属性,在 target bean 中指定 prefix,然后初始化一个 List 或者 Set 队列进行加载,比如我们将在上述的配置 my.servers
1 | (prefix="my") |
Exposing YAML as properties in the Spring Environment
The
YamlPropertySourceLoaderclass can be used to expose YAML as aPropertySourcein the Spring Environment. This allows you to use the familiar@Valueannotation with placeholders syntax to access YAML properties.
Multi-profile YAML documents
You can specify multiple profile-specific YAML documents in a single file by using a spring.profiles key to indicate when the document applies. For example:
1 | server: |
In the example above, the server.address property will be 127.0.0.1 if the development profile is active.
If the development and production profiles are not enabled, then the value for the property will be 192.168.1.100.
YAML shortcomings 短板
YAML files can’t be loaded via the @PropertySource annotation. So in the case that you need to load values that way, you need to use a properties file.
Merging YAML lists
定义了同一个 yaml 属性,在不同的 profiling 的情况下,yaml 的属性是如何转换的。这点对于不同环境如何使用不同的配置,至关重要。
Type-safe Configuration Properties
1 | import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; |
通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注册
1 |
|
application.yml 需要进行严格的配置,否则通过 FooProperties 进行加载会报错
1 | foo: |
可以直接将 @ConfigurationProperties 对象作为一个 bean 进行注入
1 |
|
Third-party configuration
上面是把 yaml 配置和 bean 的对应关系通过 bean 来配置的,其实也可以通过方法来配置,这样,可以将配置文件通过 getter 提供给第三方使用
1 | (prefix = "bar") |
Any property defined with the bar prefix will be mapped onto that BarComponent bean in a similar manner as the FooProperties example above
Relaxed binding
一种比较宽松的绑定方式,可以通过context-path绑定为 java 属性contextPath
1 | (prefix="person") |
下面对应的配置属性都可以被匹配
person.firstName
person.first-name
person.fisrt_name
PERSON_FIRST_NAME
Properties conversion
Spring will attempt to coerce the external application properties to the right type when it binds to the
@ConfigurationPropertiesbeans
当外部的应用属性通过@ConfigurationProperties被绑定以后,Spring 会试图强制的将属性转换成 java 所对应的类型的属性;
If you need custom type conversion you can provide a
ConversionServicebean (with bean idconversionService) or custom property editors (via aCustomEditorConfigurerbean) or customConverters(with bean definitions annotated as@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding).
如果你需要自定义类型转换,三种方式可以做到,一,通过ConversionService,二、通过 custom property editors,一个 CustomEditorConfigurer bean。三,通过 custom Converters。
@ConfigurationProperties Validation
通过使用 @Validated annotation 来激活 Spring Boot 验证,
You can use JSR-303
javax.validationconstraint annotations directly on your configuration class,Simply ensure that a compliant JSR-303 implementation is on your classpath, then add constraint annotations to your fields:
1 | (prefix="foo") |
In order to validate values of nested properties, you must annotate the associated field as @Valid to trigger its validation. For example, building upon the above FooProperties example:
要能够验证嵌套属性,你必须将对应的属性声明为 @Valid 才可以激活验证
1 | (prefix="connection") |
security 是一个嵌套属性,所以,必须对它声明为 @Valid
You can also add a custom Spring
Validatorby creating a bean definition calledconfigurationPropertiesValidator
你也可以通过configurationPropertiesValidator自定义 Spring Validator。
@ConfigurationProperties vs. @Value
@Value is a core container feature and it does not provide the same features as type-safe Configuration Properties.
@Value 是核心容器的特性,它不提供类型安全配置属性(type-safe Configuration Properties)的特性;
The table below summarizes the features that are supported by @ConfigurationProperties and @Value:
| Feature | @ConfigurationProperties | @Value |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxed binding | Yes | No |
| Meta-data support | Yes | No |
SpEL evaluation |
Yes | No |
25 Profiles
Spring Profiles provide a way to segregate parts of your application configuration and make it only available in certain environments. Any
@Componentor@Configurationcan be marked with@Profileto limit when it is loaded:
Spring Prifiles 提供这样一种方式来区分不同的应用配置,并且可以将这些不同的配置分别应用在不同的环境中;任何的@Component或者@Configuration注解都可以被标注@Profile
1 |
|
or in application.properties
1 | spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb |
or using the command line --spring.profiles.active=dev,hsqldb
Adding active profiles
- Java API:
setAdditionalProfiles() 通过 Command Line switch 切换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12---
my.property: fromyamlfile
---
spring.profiles: prod
spring.profiles.include:
+ proddb
+ prodmq
---
spring.profiles: dev
spring.profiles.include:
+ devdb
+ devmqwhen an application with following properties is run using the switch –spring.profiles.active=prod the proddb and prodmq profiles will also be activated:
再看一个例子1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15server:
port: 9000
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 9001
---
spring:
profiles: prod
server:
port: 0In this example the default port is 9000, but if the Spring profile ‘development’ is active then the port is 9001, and if ‘production’ is active then it is 0.
To do the same thing with properties files you can useapplication-${profile}.propertiesto specify profile-specific values.
26. Logging
27. Developing web applications
Most web applications will use the
spring-boot-starter-webmodule to get up and running quickly.
The ‘Spring Web MVC framework’
Spring MVC auto-configuration
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features, and you just want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers etc.) you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without @EnableWebMvc.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
HttpMessageConverters
Spring MVC uses the
HttpMessageConverterinterface to convert HTTP requests and responsesIf you need to add or customize converters you can use Spring Boot’s
HttpMessageConvertersclass:
1 | import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConverters; |
Any HttpMessageConverter bean that is present in the context will be added to the list of converters. You can also override default converters that way.
Custom JSON Serializers and Deserializers
Spring Boot provides an alternative
@JsonComponentannotation which makes it easier to directly register Spring Beans. You can use@JsonComponentdirectly onJsonSerializerorJsonDeserializerimplementations. You can also use it on classes that contains serializers/deserializers as inner-classes. For example:
1 | import java.io.*; |
All
@JsonComponentbeans in theApplicationContextwill be automatically registered with Jackson, and since@JsonComponentis meta-annotated with@Component, the usual component-scanning rules apply.
Spring Boot also provides
JsonObjectSerializerandJsonObjectDeserializerbase classes which provide useful alternatives to the standard Jackson versions when serializing Objects. See the Javadoc for details.
MessageCodesResolver
Spring MVC has a strategy for generating error codes for
renderingerror messages from binding errors:MessageCodesResolver. Spring Boot will create one for you if you set thespring.mvc.message-codes-resolver.formatpropertyPREFIX_ERROR_CODEorPOSTFIX_ERROR_CODE(see the enumeration in DefaultMessageCodesResolver.Format).
注意是设置错误消息返回样式的..
Static Content
By default Spring Boot will serve static content from a directory called
/static(or/publicor/resourcesor/META-INF/resources) in the classpath or from the root of theServletContext. It uses theResourceHttpRequestHandlerfrom Spring MVC so you can modify that behavior by adding your ownWebMvcConfigurerAdapterand overriding theaddResourceHandlersmethod.
默认的,Spring Boot 会以 classpath 或者
ServletContext为根路径下的/static或者/public或者/resources或者/META-INF/resources目录下的资源为静态资源;静态资源是通过ResourceHttpRequestHandler来进行处理的,你也可以通过添加你自己的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,使用重载addResourceHandlers的方式来添加你自己处理静态资源的方式。
1 | spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/resources/** |
让我一直疑虑的地方是,如果将静态资源打包在 jar 中,客户端能否缓存 css/js 等文件?
本章节提到另外一种静态资源的实现,通过 Webjars content
其实,静态资源放到 Spring BOOT 中,都不是最佳的选择,放到 Nginx 中是最好的。
Custom Favicon
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer
Spring MVC uses a
WebBindingInitializerto initialize aWebDataBinderfor a particular request. If you create your ownConfigurableWebBindingInitializer@Bean, Spring Boot will automatically configure Spring MVC to use it.
Template engines
Spring Boot includes auto-configuration support for the following templating engines:
FreeMarker
Groovy
Thymeleaf
Mustache
When you’re using one of these templating engines with the default configuration, your templates will be picked up automatically from
src/main/resources/templates.
Error Handling
Spring Boot provides an
/errormapping by default that handles all errors in a sensible way, and it is registered as a ‘global’ error page in the servlet container.For machine clients it will produce a JSON response with details of the error, the HTTP status and the exception message.
For browser clients there is a ‘whitelabel’ error view that renders the same data in HTML format (to customize it just add a View that resolves to ‘error’).
You can also define a
@ControllerAdviceto customize the JSON document to return for a particular controller and/or exception type.
1 | (basePackageClasses = FooController.class) |
In the example above, if
YourExceptionis thrown by a controller defined in the same package as FooController, a json representation of theCustomerErrorTypePOJO will be used instead of theErrorAttributesrepresentation.
可以捕获你自己定义的异常YourException,并且通过自定义CustomErrorType JSON 徐哦呜消息格式来替换默认的ErrorAttributes错误消息格式。
Custom error pages
Mapping error pages outside of Spring MVC
Spring HATEOAS
处理超媒体用的..
CORS support
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a W3C specification implemented by most browsers that allows you to specify in a flexible way what kind of cross domain requests are authorized, instead of using some less secure and less powerful approaches like IFRAME or JSONP.
CORS 是一种比使用 IFRAME 或者 JSONP 更为健壮的跨域的解决方案。
Global CORS configuration can be defined by registering a WebMvcConfigurer bean with a customized addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry) method:
1 |
|
JAX-RS and Jersey
Embedded servlet container support
Spring Boot includes support for embedded Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow servers. Most developers will simply use the appropriate ‘Starter’ to obtain a fully configured instance. By default the embedded server will listen for HTTP requests on port 8080.
Spring Boot 有内嵌的 Tomcat, Jetty, Undertow 等 web 服务器,可以通过简单的使用 “Starter” 就可以获取他们。
(If you choose to use Tomcat on CentOS be aware that, by default, a temporary directory is used to store compiled JSPs, file uploads etc. This directory may be deleted by
tmpwatchwhile your application is running leading to failures. To avoid this, you may want to customize yourtmpwatchconfiguration so thattomcat.*directories are not deleted, or configureserver.tomcat.basedirso that embedded Tomcat uses a different location.)
Servlets, Filters, and listeners
Servlet Context Initialization
Embedded servlet containers will not directly execute the Servlet 3.0+
javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializerinterface, or Spring’sorg.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializerinterface.`
If you need to perform servlet context initialization in a Spring Boot application, you should register a bean that implements the
org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ServletContextInitializerinterface. The singleonStartupmethod provides access to theServletContext, and can easily be used as an adapter to an existingWebApplicationInitializerif necessary.
Scanning for Servlets, Filters, and listeners
When using an embedded container, automatic registration of @WebServlet, @WebFilter, and @WebListener annotated classes can be enabled using @ServletComponentScan.
The EmbeddedWebApplicationContext
Under the hood Spring Boot uses a new type of
ApplicationContextfor embedded servlet container support.
The
EmbeddedWebApplicationContextis a special type ofWebApplicationContextthat bootstraps itself by searching for a singleEmbeddedServletContainerFactorybean. Usually aTomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory,JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory, orUndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactorywill have been auto-configured.
Customizing embedded servlet containers
Common servlet container settings can be configured using Spring
Environmentproperties. Usually you would define the properties in yourapplication.propertiesfile.
可以通过application.properties来设置嵌入的 servlet 容器,可以设置 IP,PORT,SESSION,server.error.path,SSL,HTTP compression
Programmatic customization
If you need to configure your embedded servlet container programmatically you can register a Spring bean that implements the
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerinterface.EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerprovides access to theConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainerwhich includes numerous customization setter methods.
1 | import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.*; |
Customizing ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer directly
If the above customization techniques are too limited, you can register the TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory, JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory or UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean yourself.
1 |
|
还是通过配置来改变是正道,这里通过程序来改变最大的问题是不能通用。
JSP limitations
当使用嵌入容器执行 JSP 的时候有一些限制,
JSP Tomcat 可以在 WAR 中执行,但是在 JAR 中不行
28. Security
33. Calling REST services
If you need to call remote REST services from your application, you can use Spring Framework’s
RestTemplateclass. SinceRestTemplateinstances often need to be customized before being used, Spring Boot does not provide any single auto-configuredRestTemplatebean. It does, however, auto-configure aRestTemplateBuilderwhich can be used to createRestTemplateinstances when needed. The auto-configured RestTemplateBuilder will ensure that sensible HttpMessageConverters are applied toRestTemplateinstances.
这章节重要了,讲述了作为客户端如何去调用 REST 接口;Spring Boot 是通过自动配置一个RestTemplateBuilder实例,可以通过它生成RestTemplate实例;
1 |
|
我的疑问是,为什么每次都要通过restTemplateBuilder.build()去获得一个restTemplate? 我的理解是,既然restTemplate是全局单例的,那么直接在容器里面注册一个restTemplate直接使用不是更好?
RestTemplate customization
There are three main approaches to
RestTemplatecustomization, depending on how broadly you want the customizations to apply.
To make the scope of any customizations as narrow as possible, inject the auto-configured
RestTemplateBuilderand then call its methods as required. Each method call returns a newRestTemplateBuilderinstance so the customizations will only affect this use of the builder.
RestTemplateBuilder被设计成不是单例模式,目的就是为了接受不同的特有配置;
To make an application-wide, additive customization a
RestTemplateCustomizerbean can be used. All such beans are automatically registered with the auto-configuredRestTemplateBuilderand will be applied to any templates that are built with it.
可以通过RestTemplateCustomizer bean 自定义全局适配的规则,然后这些自定义的 bean 会自动注册到 RestTemplateBuilder
1 | static class ProxyCustomizer implements RestTemplateCustomizer { |
疑问,ProxyCustomizer 是怎么加入 Spring 容器的?供RestTemplateBuilder使用的?
34. Validation
35. Sending email
36. Distributed Transactions with JTA
37. Hazelcast
38. Spring Integration
39. Spring Session
Spring Boot provides Spring Session auto-configuration for a wide range of stores:
- JDBC
- MongoDB
- Redis
- Hazelcast
- HashMap
1 | spring.session.store-type=jdbc |
管理 Http Session,
http://projects.spring.io/spring-session/
http://www.cnblogs.com/mengmeng89012/p/5519698.html
40. Monitoring and management over JMX
41. Testing
spring-boot-testcontains core items 和spring-boot-test-autoconfiguresupports auto-configuration for tests.
Most developers will just use the
spring-boot-starter-test‘Starter’ which imports both Spring Boot test modules as well has JUnit, AssertJ, Hamcrest and a number of other useful libraries.
Test scope dependencies
If you use the spring-boot-starter-test ‘Starter’ (in the test scope), you will find the following provided libraries:
JUnit — The de-facto standard for unit testing Java applications.
Spring Test & Spring Boot Test — Utilities and integration test support for Spring Boot applications.
AssertJ — A fluent assertion library.
Hamcrest — A library of matcher objects (also known as constraints or predicates).
Mockito — A Java mocking framework.
JSONassert — An assertion library for JSON.
JsonPath — XPath for JSON.
Testing Spring applications
One of the major advantages of dependency injection is that it should make your code easier to unit test. You can simply instantiate objects using the
newoperator without even involving Spring. You can also use mock objects instead of real dependencies.
If you have not used the spring-test module before you should start by reading the relevant section of the Spring Framework reference documentation.
Testing Spring Boot applications
Spring Boot provides a @SpringBootTest annotation which can be used as an alternative to the standard spring-test @ContextConfiguration annotation when you need Spring Boot features.
Detecting test configuration
Excluding test configuration
Spring Boot provides
@TestComponentand@TestConfigurationannotations that can be used on classes insrc/test/javato indicate that they should not be picked up by scanning.
当被注释为@TestComponent和@TestConfiguration的实例,表示只会在测试的时候被加载。
Working with random ports
If you need to start a full running server for tests, we recommend that you use random ports. If you use
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment=WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)an available port will be picked at random each time your test runs.
如果你需要启动 web server 测试,建议使用@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment=WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)为每一次启动开启一个任意的端口。
Mocking and spying beans
It’s sometimes necessary to mock certain components within your application context when running tests. For example, you may have a facade over some remote service that’s unavailable during development. Mocking can also be useful when you want to simulate failures that might be hard to trigger in a real environment.
一段话就道出了为什么我们要使用 mock 的原因,比如,你有一个接口依赖远程实现,但是远程实现并未完成,你就需要 mock。
Spring Boot includes a
@MockBeanannotation that can be used to define a Mockito mock for a bean inside yourApplicationContext. You can use the annotation to add new beans, or replace a single existing bean definition. The annotation can be used directly on test classes, on fields within your test, or on @Configuration classes and fields. When used on a field, the instance of the created mock will also be injected. Mock beans are automatically reset after each test method.
通过@MockBean注解可以在ApplicationContext中定义一个通过 Mockito mock 的 bean;你可以使用该注解添加新的 beans,或者替换一个存在的 bean。该注解可以直接使用再你的测试类,a fileds 或者是 @Configuration classes and fields. 当你使用 field,所创建的 mock 实例将会被注入。Mock beans 在每一次测试完成后将会被自动的重置。
1 | import org.junit.*; |
这里通过@MockBean注入 RemoteService
Additionally you can also use @SpyBean to wrap any existing bean with a Mockito spy. See the Javadoc for full details.
Auto-configured tests
Spring Boot’s auto-configuration system works well for applications, but can sometimes be a little too much for tests. It’s often helpful to load only the parts of the configuration that are required to test a ‘slice’ of your application.
有时候我们只需要加载配置中的一部分来完成一部分功能的验证即可,
For example, you might want to test that Spring MVC controllers are mapping URLs correctly, and you don’t want to involve database calls in those tests; or you might be wanting to test JPA entities, and you’re not interested in web layer when those tests run.
比如,你可能指向验证 controllers 是否正确映射了所有的 URLs,你并不想把数据库的调用给加载进来。
The
spring-boot-test-autoconfiguremodule includes a number of annotations that can be used to automatically configure such ‘slices’. Each of them works in a similar way, providing a@…Testannotation that loads theApplicationContextand one or more@AutoConfigure…annotations that can be used to customize auto-configuration settings.
spring-boot-test-autoconfigure可以帮助你完成上述请求…
Auto-configured JSON tests
To test that Object JSON serialization and deserialization is working as expected you can use the
@JsonTestannotation.
@JsonTest 专门用来测试 JSON 的序列化和反序列化行为的。
@JsonTestwill auto-configure JacksonObjectMapper, any@JsonComponentbeans and any JacksonModules.
@JsonTest将会自动的配置 Jackson ObjectMapper,任何的@JsonComponent以及Jackson Modules
The
JacksonTester,GsonTesterandBasicJsonTesterclasses can be used forJackson,GsonandStringsrespectively.
下面这个例子将会使用JacksonTester来做测试
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
Auto-configured Spring MVC tests
To test Spring MVC controllers are working as expected you can use the
@WebMvcTestannotation.@WebMvcTestwill auto-configure the Spring MVC infrastructure and limit scanned beans to@Controller,@ControllerAdvice,@JsonComponent,Filter,WebMvcConfigurerandHandlerMethodArgumentResolver. Regular@Componentbeans will not be scanned when using this annotation.
使用 @WebMvcTest 将会自动的加载 MVC 相应的 controllers,但是不会加载 @Component bean
Auto-configured Data JPA tests
@DataJpaTestcan be used if you want to test JPA applications
Auto-configured JDBC tests
@JdbcTestis similar to @DataJpaTest but for pure jdbc-related tests. By default it will also configure an in-memory embedded database and aJdbcTemplate,
JDBC tests are transactional and rollback at the end of each test by default
@JdbcTest声明的测试用例默认是在事务环境下,执行完成以后便回滚。
当然,你也可以手动设计为不会滚,见如下测试用例
1 | import org.junit.Test; |
If you prefer your test to run against a real database, you can use the @AutoConfigureTestDatabase annotation the same way as for DataJpaTest.
Auto-configured Data MongoDB tests
Auto-configured REST clients
The @RestClientTest annotation can be used if you want to test REST clients. By default it will auto-configure Jackson and GSON support, configure a RestTemplateBuilder and add support for MockRestServiceServer, The specific beans that you want to test should be specified using value or components attribute of @RestClientTest:
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
Auto-configured Spring REST Docs tests
The
@AutoConfigureRestDocsannotation can be used if you want to use Spring REST Docs in your tests. It will automatically configureMockMvcto use Spring REST Docs and remove the need for Spring REST Docs’ JUnit rule.
Spring REST Docs? 什么东西?难道要测试 REST 文档?
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
@AutoConfigureRestDocscan be used to override the default output directory (target/generated-snippetsif you are using Maven orbuild/generated-snippetsif you are using Gradle). It can also be used to configure the host, scheme, and port that will appear in any documented URIs. If you require more control over Spring REST Docs’ configuration aRestDocsMockMvcConfigurationCustomizerbean can be used:
1 |
|
If you want to make use of Spring REST Docs’ support for a
parameterizedoutput directory, you can create aRestDocumentationResultHandlerbean. The auto-configuration will callalwaysDowith this result handler, thereby causing eachMockMvccall to automatically generate the default snippets:
1 |
|
Ok, 通读完所有文档以后,明白了,是为了测试 REST 接口文档的规范、格式等;可以单独针对某一个方法进行测试;
Using Spock to test Spring Boot applications
Test utilities
ConfigFileApplicationContextInitializer
ConfigFileApplicationContextInitializeris anApplicationContextInitializerthat can apply to your tests to load Spring Bootapplication.propertiesfiles. You can use this when you don’t need the full features provided by@SpringBootTest.
1 | (classes = Config.class, |
EnvironmentTestUtils
EnvironmentTestUtilsallows you to quickly add properties to aConfigurableEnvironmentorConfigurableApplicationContext. Simply call it withkey=valuestrings:
1 | EnvironmentTestUtils.addEnvironment(env, "org=Spring", "name=Boot"); |
OutputCapture
OutputCaptureis a JUnit Rule that you can use to captureSystem.outandSystem.erroutput. Simply declare the capture as a@Rulethen usetoString()for assertions:
1 | import org.junit.Rule; |
重点看看这个玩意儿org.hamcrest.Matchers,正则表达式的工具类。
TestRestTemplate
TestRestTemplateis a convenience alternative to Spring’sRestTemplatethat is useful in integration tests. You can get a vanilla template or one that sends Basic HTTP authentication (with a username and password). In either case the template will behave in a test-friendly way: not following redirects (so you can assert the response location), ignoring cookies (so the template is stateless), and not throwing exceptions on server-side errors. It is recommended, but not mandatory, to use Apache HTTP Client (version 4.3.2 or better), and if you have that on your classpath the TestRestTemplate will respond by configuring the client appropriately.
1 | public class MyTest { |
If you are using the
@SpringBootTestannotation withWebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORTorWebEnvironment.DEFINED_PORT, you can just inject a fully configuredTestRestTemplateand start using it. If necessary, additional customizations can be applied via theRestTemplateBuilderbean:
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
通过动态注入TestRestTemplate可以自动获取端口?
WebSockets
Spring Boot provides WebSockets auto-configuration for
embeddedTomcat (8 and 7), Jetty 9 and Undertow.
如果是通过嵌入式的 Tomcat,Spring Boot 将自动配置提供 WebSockets。
Spring Framework provides rich WebSocket support that can be easily accessed via the spring-boot-starter-websocket module.
If you’re deploying a war file to a standalone container, Spring Boot assumes that the container will be responsible for the configuration of its WebSocket support.
WebServices
The Spring Web Services features can be easily accessed via the spring-boot-starter-webservices module.
Creating your own auto-configuration
Auto-configuration can be associated to a “starter” that provides the auto-configuration code as well as the typical libraries that you would use with it. We will first cover what you need to know to build your own auto-configuration and we will move on to the typical steps required to create a custom starter.
搞个半天,原来 auto-configuration 就是指的 starter
A demo project is available to showcase how you can create a starter step by step.
Understanding auto-configured beans
Under the hood, auto-configuration is implemented with standard
@Configurationclasses.
Locating auto-configuration candidates
Spring Boot checks for the presence of a
META-INF/spring.factoriesfile within your published jar. The file should list your configuration classes under theEnableAutoConfigurationkey.